线程池并发服务器
为什么要引入线程池,不直接用之前的多线程并发?
因为多线程并发要频繁地对线程进行创建与销毁(一旦有客户端传来需求,就创建一个新线程,通信结束就立刻销毁该线程),这会占用大量的CPU时间并导致不必要的系统开销
相关结构体
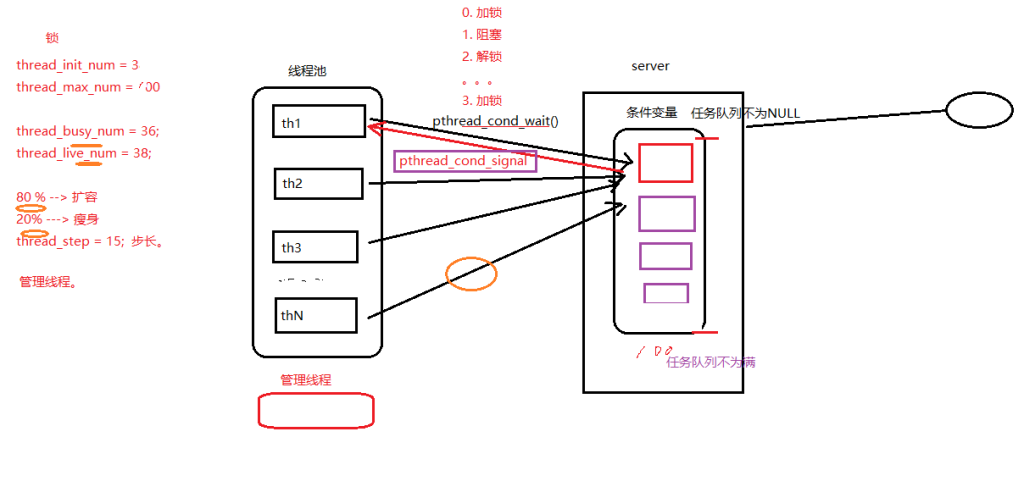
线程池结构体:描述线程池相关信息
pthread_mutex_t lock; /* 用于锁住本结构体 */
pthread_mutex_t thread_counter; /* 记录忙状态线程个数的锁 -- busy_thr_num */
pthread_cond_t queue_not_full; /* 当任务队列满时,添加任务的线程阻塞,等待此条件变量 */
pthread_cond_t queue_not_empty; /* 任务队列里不为空时,通知等待任务的线程 */
pthread_t *threads; /* 数组,存放线程池中每个线程的tid */
pthread_t adjust_tid; /* 存管理线程的tid */
threadpool_task_t *task_queue; /* 任务队列(自定义任务队列结构体数组首地址) */
int min_thr_num; /* 线程池最小线程数 */
int max_thr_num; /* 线程池最大线程数 */
int live_thr_num; /* 当前存活线程个数 */
int busy_thr_num; /* 忙状态线程个数 */
int wait_exit_thr_num; /* 要销毁的线程个数 */
int queue_front; /* task_queue队头下标 */
int queue_rear; /* task_queue队尾下标 */
int queue_size; /* task_queue队中实际任务数 */
int queue_max_size; /* task_queue队列可容纳任务数上限 */
int shutdown; /* 标志位,线程池使用状态,是否关闭线程池,true或false */任务队列结构体:在线程池结构体中充当任务队列
typedef struct {
void *(*function)(void *); /* 函数指针,回调函数 */
void *arg; /* 上面函数的参数 */
} threadpool_task_t; /* 各子线程任务结构体 */线程池模块分析
- main()
- 创建线程池
- 向线程池中添加任务(即给线程池中的线程分配任务),借助回调函数处理任务
- 销毁线程池。
- threadpool_create()
- 创建线程池结构体指针
- 初始化线程池结构体
- 创建n个任务线程
- 创建1个管理者线程
- 失败时,销毁开辟的所有空间(释放)
- threadpool_thread() part1
- 进入子线程回调函数
- 接收参数void *arg,即pool结构体
- 对lock进行加锁(即锁住整个结构体的那个锁)
- 判断条件变量→wait
- adjust_thread()
- 进入管理者线程回调函数
- 循环10s执行一次(管理者不用一直盯着)
- 接收参数void *arg,即pool结构体
- 对lock进行加锁
- 获取管理线程池要用到的变量:task_num、live_num、busy_num
- 根据既定算法,使用上述三个变量,判断是否应该创建、销毁线程池中指定步长数的线程
- threadpool_add():
- 对lock进行加锁
- 初始化任务队列结构体成员:设置回调函数function与函数参数arg
- 利用环形队列机制(移动队尾指针和取余操作),实现添加任务,即入队
- 唤醒阻塞在条件变量queue_not_empty上的线程
- 解锁
- threadpool_thread() part2
- 从3.中的wait之后继续执行
- 获取任务处理回调函数及其参数
- 利用环形队列机制(移动队头指针和取余操作),实现处理任务,即出队
- 唤醒阻塞在条件变量queue_not_full上的server
- 对lock进行解锁
- 对thread_counter加锁
- 修改忙线程数++
- 对thread_counter解锁
- 执行处理任务的线程
- 对thread_counter加锁
- 修改忙线程数–
- 对thread_counter解锁
- 扩容/瘦身
- 当满足扩容条件时:
- 执行pthread_create()
- 回调任务线程函数
- live_num++
- 当满足瘦身条件时:
- 设置wait_exit_thr_num = 10;
- 给阻塞在条件变量queue_not_empty上的线程发送假条件满足信号
- 阻塞线程会被假信号唤醒,执行销毁流程:判断wait_exit_thr_num > 0→pthread_exit();
- 当满足扩容条件时:
实现代码
//能看懂即可
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include "threadpool.h"
#define DEFAULT_TIME 10 /*10s检测一次*/
#define MIN_WAIT_TASK_NUM 10 /*如果queue_size > MIN_WAIT_TASK_NUM 添加新的线程到线程池*/
#define DEFAULT_THREAD_VARY 10 /*每次创建和销毁线程的个数*/
#define true 1
#define false 0
typedef struct {
void *(*function)(void *); /* 函数指针,回调函数 */
void *arg; /* 上面函数的参数 */
} threadpool_task_t; /* 各子线程任务结构体 */
/* 描述线程池相关信息 */
struct threadpool_t {
pthread_mutex_t lock; /* 用于锁住本结构体 */
pthread_mutex_t thread_counter; /* 记录忙状态线程个数de琐 -- busy_thr_num */
pthread_cond_t queue_not_full; /* 当任务队列满时,添加任务的线程阻塞,等待此条件变量 */
pthread_cond_t queue_not_empty; /* 任务队列里不为空时,通知等待任务的线程 */
pthread_t *threads; /* 存放线程池中每个线程的tid。数组 */
pthread_t adjust_tid; /* 存管理线程tid */
threadpool_task_t *task_queue; /* 任务队列(数组首地址) */
int min_thr_num; /* 线程池最小线程数 */
int max_thr_num; /* 线程池最大线程数 */
int live_thr_num; /* 当前存活线程个数 */
int busy_thr_num; /* 忙状态线程个数 */
int wait_exit_thr_num; /* 要销毁的线程个数 */
int queue_front; /* task_queue队头下标 */
int queue_rear; /* task_queue队尾下标 */
int queue_size; /* task_queue队中实际任务数 */
int queue_max_size; /* task_queue队列可容纳任务数上限 */
int shutdown; /* 标志位,线程池使用状态,true或false */
};
void *threadpool_thread(void *threadpool);
void *adjust_thread(void *threadpool);
int is_thread_alive(pthread_t tid);
int threadpool_free(threadpool_t *pool);
//threadpool_create(3,100,100);
threadpool_t *threadpool_create(int min_thr_num, int max_thr_num, int queue_max_size)
{
int i;
threadpool_t *pool = NULL; /* 线程池 结构体 */
do {
if((pool = (threadpool_t *)malloc(sizeof(threadpool_t))) == NULL) {
printf("malloc threadpool fail");
break; /*跳出do while*/
}
pool->min_thr_num = min_thr_num;
pool->max_thr_num = max_thr_num;
pool->busy_thr_num = 0;
pool->live_thr_num = min_thr_num; /* 活着的线程数 初值=最小线程数 */
pool->wait_exit_thr_num = 0;
pool->queue_size = 0; /* 有0个产品 */
pool->queue_max_size = queue_max_size; /* 最大任务队列数 */
pool->queue_front = 0;
pool->queue_rear = 0;
pool->shutdown = false; /* 不关闭线程池 */
/* 根据最大线程上限数, 给工作线程数组开辟空间, 并清零 */
pool->threads = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t)*max_thr_num);
if (pool->threads == NULL) {
printf("malloc threads fail");
break;
}
memset(pool->threads, 0, sizeof(pthread_t)*max_thr_num);
/* 给 任务队列 开辟空间 */
pool->task_queue = (threadpool_task_t *)malloc(sizeof(threadpool_task_t)*queue_max_size);
if (pool->task_queue == NULL) {
printf("malloc task_queue fail");
break;
}
/* 初始化互斥琐、条件变量 */
if (pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->lock), NULL) != 0
|| pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->thread_counter), NULL) != 0
|| pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_not_empty), NULL) != 0
|| pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_not_full), NULL) != 0)
{
printf("init the lock or cond fail");
break;
}
/* 启动 min_thr_num 个 work thread */
for (i = 0; i < min_thr_num; i++) {
pthread_create(&(pool->threads[i]), NULL, threadpool_thread, (void *)pool); /*pool指向当前线程池*/
printf("start thread 0x%x...\n", (unsigned int)pool->threads[i]);
}
pthread_create(&(pool->adjust_tid), NULL, adjust_thread, (void *)pool); /* 创建管理者线程 */
return pool;
} while (0);
threadpool_free(pool); /* 前面代码调用失败时,释放pool存储空间 */
return NULL;
}
/* 向线程池中 添加一个任务 */
//threadpool_add(thp, process, (void*)&num[i]); /* 向线程池中添加任务 process: 小写---->大写*/
int threadpool_add(threadpool_t *pool, void*(*function)(void *arg), void *arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
/* ==为真,队列已经满, 调wait阻塞 */
while ((pool->queue_size == pool->queue_max_size) && (!pool->shutdown)) {
pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_not_full), &(pool->lock));
}
if (pool->shutdown) {
pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
return 0;
}
/* 清空 工作线程 调用的回调函数 的参数arg */
if (pool->task_queue[pool->queue_rear].arg != NULL) {
pool->task_queue[pool->queue_rear].arg = NULL;
}
/*添加任务到任务队列里*/
pool->task_queue[pool->queue_rear].function = function;
pool->task_queue[pool->queue_rear].arg = arg;
pool->queue_rear = (pool->queue_rear + 1) % pool->queue_max_size; /* 队尾指针移动, 模拟环形 */
pool->queue_size++;
/*添加完任务后,队列不为空,唤醒线程池中 等待处理任务的线程*/
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
return 0;
}
/* 线程池中各个工作线程 */
void *threadpool_thread(void *threadpool)
{
threadpool_t *pool = (threadpool_t *)threadpool;
threadpool_task_t task;
while (true) {
/* Lock must be taken to wait on conditional variable */
/*刚创建出线程,等待任务队列里有任务,否则阻塞等待任务队列里有任务后再唤醒接收任务*/
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
/*queue_size == 0 说明没有任务,调 wait 阻塞在条件变量上, 若有任务,跳过该while*/
while ((pool->queue_size == 0) && (!pool->shutdown)) {
printf("thread 0x%x is waiting\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());
pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_not_empty), &(pool->lock));
/*清除指定数目的空闲线程,如果要结束的线程个数大于0,结束线程*/
if (pool->wait_exit_thr_num > 0) {
pool->wait_exit_thr_num--;
/*如果线程池里线程个数大于最小值时可以结束当前线程*/
if (pool->live_thr_num > pool->min_thr_num) {
printf("thread 0x%x is exiting\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());
pool->live_thr_num--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
}
}
/*如果指定了true,要关闭线程池里的每个线程,自行退出处理---销毁线程池*/
if (pool->shutdown) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
printf("thread 0x%x is exiting\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
pthread_exit(NULL); /* 线程自行结束 */
}
/*从任务队列里获取任务, 是一个出队操作*/
task.function = pool->task_queue[pool->queue_front].function;
task.arg = pool->task_queue[pool->queue_front].arg;
pool->queue_front = (pool->queue_front + 1) % pool->queue_max_size; /* 出队,模拟环形队列 */
pool->queue_size--;
/*通知可以有新的任务添加进来*/
pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_not_full));
/*任务取出后,立即将 线程池琐 释放*/
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
/*执行任务*/
printf("thread 0x%x start working\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter)); /*忙状态线程数变量琐*/
pool->busy_thr_num++; /*忙状态线程数+1*/
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->thread_counter));
(*(task.function))(task.arg); /*执行回调函数任务*/
//task.function(task.arg); /*执行回调函数任务*/
/*任务结束处理*/
printf("thread 0x%x end working\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter));
pool->busy_thr_num--; /*处理掉一个任务,忙状态数线程数-1*/
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->thread_counter));
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
/* 管理线程 */
void *adjust_thread(void *threadpool)
{
int i;
threadpool_t *pool = (threadpool_t *)threadpool;
while (!pool->shutdown) {
sleep(DEFAULT_TIME); /*定时 对线程池管理*/
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
int queue_size = pool->queue_size; /* 关注 任务数 */
int live_thr_num = pool->live_thr_num; /* 存活 线程数 */
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter));
int busy_thr_num = pool->busy_thr_num; /* 忙着的线程数 */
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->thread_counter));
/* 创建新线程 算法: 任务数大于最小线程池个数, 且存活的线程数少于最大线程个数时 如:30>=10 && 40<100*/
if (queue_size >= MIN_WAIT_TASK_NUM && live_thr_num < pool->max_thr_num) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
int add = 0;
/*一次增加 DEFAULT_THREAD 个线程*/
for (i = 0; i < pool->max_thr_num && add < DEFAULT_THREAD_VARY
&& pool->live_thr_num < pool->max_thr_num; i++) {
if (pool->threads[i] == 0 || !is_thread_alive(pool->threads[i])) {
pthread_create(&(pool->threads[i]), NULL, threadpool_thread, (void *)pool);
add++;
pool->live_thr_num++;
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
}
/* 销毁多余的空闲线程 算法:忙线程X2 小于 存活的线程数 且 存活的线程数 大于 最小线程数时*/
if ((busy_thr_num * 2) < live_thr_num && live_thr_num > pool->min_thr_num) {
/* 一次销毁DEFAULT_THREAD个线程, 隨機10個即可 */
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
pool->wait_exit_thr_num = DEFAULT_THREAD_VARY; /* 要销毁的线程数 设置为10 */
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
for (i = 0; i < DEFAULT_THREAD_VARY; i++) {
/* 通知处在空闲状态的线程, 他们会自行终止*/
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
int threadpool_destroy(threadpool_t *pool)
{
int i;
if (pool == NULL) {
return -1;
}
pool->shutdown = true;
/*先销毁管理线程*/
pthread_join(pool->adjust_tid, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < pool->live_thr_num; i++) {
/*通知所有的空闲线程*/
pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
}
for (i = 0; i < pool->live_thr_num; i++) {
pthread_join(pool->threads[i], NULL);
}
threadpool_free(pool);
return 0;
}
int threadpool_free(threadpool_t *pool)
{
if (pool == NULL) {
return -1;
}
if (pool->task_queue) {
free(pool->task_queue);
}
if (pool->threads) {
free(pool->threads);
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pool->lock));
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter));
pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pool->thread_counter));
pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->queue_not_full));
}
free(pool);
pool = NULL;
return 0;
}
int threadpool_all_threadnum(threadpool_t *pool)
{
int all_threadnum = -1; // 总线程数
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
all_threadnum = pool->live_thr_num; // 存活线程数
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
return all_threadnum;
}
int threadpool_busy_threadnum(threadpool_t *pool)
{
int busy_threadnum = -1; // 忙线程数
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter));
busy_threadnum = pool->busy_thr_num;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->thread_counter));
return busy_threadnum;
}
int is_thread_alive(pthread_t tid)
{
int kill_rc = pthread_kill(tid, 0); //发0号信号,测试线程是否存活
if (kill_rc == ESRCH) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/*测试*/
#if 1
/* 线程池中的线程,模拟处理业务 */
void *process(void *arg)
{
printf("thread 0x%x working on task %d\n ",(unsigned int)pthread_self(),(int)arg);
sleep(1); //模拟 小---大写
printf("task %d is end\n",(int)arg);
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
/*threadpool_t *threadpool_create(int min_thr_num, int max_thr_num, int queue_max_size);*/
threadpool_t *thp = threadpool_create(3,100,100); /*创建线程池,池里最小3个线程,最大100,队列最大100*/
printf("pool inited");
//int *num = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*20);
int num[20], i;
for (i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
num[i] = i;
printf("add task %d\n",i);
/*int threadpool_add(threadpool_t *pool, void*(*function)(void *arg), void *arg) */
threadpool_add(thp, process, (void*)&num[i]); /* 向线程池中添加任务 */
}
sleep(10); /* 等子线程完成任务 */
threadpool_destroy(thp);
return 0;
}
#endifC/S模型-UDP
TCP/UDP通信对比
TCP:面向连接的,可靠数据包传输。对于不稳定的网络层,采取完全弥补的通信方式(丢包重传)
- 优点
- 数据流量稳定
- 速度稳定
- 按序
- 缺点
- 传输速度慢
- 效率低
- 开销大
- 使用场景:数据的完整型要求较高,不追求效率(大数据传输、文件传输)
UDP:无连接的,不可靠的数据报传递。对于不稳定的网络层,采取完全不弥补的通信方式(默认还原网络状况)
- 优点
- 传输速度块
- 效率高
- 开销小
- 缺点
- 数据流量不稳定
- 速度不稳定
- 不按序
- 使用场景:对时效性要求较高,稳定性其次(游戏、视频电话)
ps:QQ、微信等大型项目追求传输速度,在传输层采用UDP协议,但会在应用层补充数据校验协议,弥补UDP的不足
UDP实现的 C/S 模型
①因为UDP不用建立连接,因此服务器舍弃accpet()和connect()函数
②read()和write()函数也被舍弃,且recv()和send()函数只能用于TCP通信,因此使用recvfrom()和sendto()函数替换
③不用设计并发,UDP实现的默认就是并发服务器,因为不需要建立连接了
相关函数
ssize_t recvfrom(int sockfd, void *buf, size_t len, int flags,struct sockaddr *src_addr, socklen_t *addrlen); 接收数据,同时获取对端地址结构,相当于TCP中的read() + accept()
参数:
- sockfd:套接字
- buf:缓冲区地址
- len:缓冲区大小
- flags:0
- src_addr:传出参数,对端地址结构(如果不关心对端地址结构,一般是客户端调用该函数时,该参数传NULL)
- addrlen:传入传出参数(因此是指针类型),地址结构大小(如果不关心对端地址结构,该参数传0)
返回值:
- 成功:接收数据字节数
- 失败:-1,errno
- 0:说明对端关闭(跟read函数一样)
ssize_t sendto(int sockfd, const void *buf, size_t len, int flags,const struct sockaddr *dest_addr, socklen_t addrlen); 发送数据,相当于TCP中的write() + connect()
参数:
- sockfd: 套接字
- buf:存储数据的缓冲区
- len:数据长度
- flags:0
- src_addr:传入参数,目标地址结构
- addrlen:地址结构长度
返回值:
- 成功:成功写出数据字节数
- 失败:-1,errno
思路分析
server:
伪代码 {
lfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0); //注意第二个参数变了,改为以UDP为代表的报式协议
bind();
listen(); //可有可无(因为不需要三次握手了,也就不需要设置连接上限了)
while(1){
recvfrom()
//数据处理
sendto()
}
close();
}client:
伪代码 {
connect_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
sendto();
recvfrom();
写到屏幕
close();
}代码实现
server:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<arpa/inet.h>
#define SERV_PORT 9527
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int sockfd = 0;
int ret, i;
char buf[BUFSIZ], client_IP[1024];
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr, clit_addr;
socklen_t clit_addr_len;
bzero(&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
clit_addr_len = sizeof(clit_addr);
while(1) {
ret = recvfrom(sockfd, buf, sizeof(buf), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&clit_addr, &clit_addr_len);
//输出查看客户端地址结构
printf("client ip:%s port:%d\n",
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &clit_addr.sin_addr.s_addr, client_IP, sizeof(client_IP)),
ntohs(clit_addr.sin_port));
for(i = 0; i < ret; i++) {
buf[i] = toupper(buf[i]);
}
sendto(sockfd, buf, ret, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&clit_addr, clit_addr_len);
}
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}client:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<ctype.h>
#include<arpa/inet.h>
#define SERV_PORT 9527
#define SERV_IP "127.0.0.1"
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int sockfd = 0;
int ret;
char buf[BUFSIZ];
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr;
bzero(&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; //指定服务器的地址结构
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(SERV_PORT);
inet_pton(AF_INET, SERV_IP, &serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr);
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0);
while(1) {
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin); //从屏幕输入要让服务器处理的数据
sendto(sockfd, buf, strlen(buf), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr)); //strlen代表从屏幕写入数据后缓冲区实际的大小,而不是容量
ret = recvfrom(sockfd, buf, sizeof(buf), 0, NULL, 0); //用不到对端服务器的地址结构了,传出参数传NULL
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, ret);
}
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}socket IPC(本地套接字domin)
概论
IPC方法: pipe、fifo、mmap、信号、本地套接字(domain)
对比网络编程TCP C/S模型, 注意以下几点:
- int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol);
- domain:AF_INET改为AF_UNIX/AF_LOCAL
- type:SOCK_STREAM或SOCK_DGRAM都可以
- protocol:依然默认传0
- 地址结构类型由so ckaddr_in改为sockaddr_un,依然是结构体,但只有两个成员变量
- struct sockaddr_in srv_addr; → struct sockaddr_un srv_adrr;
- srv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; → srv_addr.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
- srv_addr.sin_port = htons(8888);srv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); → strcpy(srv_addr.sun_path, SERV_ADDR)
- struct sockaddr_in srv_addr; → struct sockaddr_un srv_adrr;
- bind()函数的第三个参数不能用sizeof()
- len = offsetof(struct sockaddr_un, sun_path) + strlen(srvaddr.sun_path); //sockaddr_un中16位的sun_family+路径文件名sun_path大小
- offsetof函数作用是求结构体struct sockaddr_un中第二个成员变量sun_path偏移了多少,也就是求第一个成员变量sun_family的大小
- 既然知道sun_family大小是16位,为什么不把offsetof(struct sockaddr_un, sun_path)直接写成2呢?因为不让,那样就成硬编码了
- bind(fd, (struct sockaddr *)&srv_addr, sizeof(srv_addr)); → bind(fd, (struct sockaddr *)&srv_addr, len);
- len = offsetof(struct sockaddr_un, sun_path) + strlen(srvaddr.sun_path); //sockaddr_un中16位的sun_family+路径文件名sun_path大小
- 在本地套接字中,bind()函数调用成功后会创建一个socket,因此为保证bind()成功,通常我们在bind()之前,可以使用unlink(SERV_ADDR)将路径文件名删除,确保在bind()前serv.sock文件不存在
- 客户端不能依赖“隐式绑定”,因此在通信建立过程中,需要创建并初始化两个地址结构:①client_addr用于bind()生成套接字 ②server_addr用于connect()连接通信
代码实现
server
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include "wrap.h"
#define SERV_ADDR "serv.socket"
int main(void) {
int lfd, cfd, len, size, i;
struct sockaddr_un servaddr, cliaddr;
char buf[4096];
lfd = Socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
servaddr.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(servaddr.sun_path, SERV_ADDR);
len = offsetof(struct sockaddr_un, sun_path) + strlen(servaddr.sun_path); /* servaddr total len */
unlink(SERV_ADDR); /* 确保bind之前serv.sock文件不存在,bind会创建该文件 */
Bind(lfd, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, len); /* 参3不能是sizeof(servaddr) */
Listen(lfd, 20);
printf("Accept ...\n");
while (1) {
len = sizeof(cliaddr); //AF_UNIX大小+108B
cfd = Accept(lfd, (struct sockaddr *)&cliaddr, (socklen_t *)&len);
len -= offsetof(struct sockaddr_un, sun_path); /* 得到文件名的长度 */
cliaddr.sun_path[len] = '\0'; /* 确保打印时,没有乱码出现 */
printf("client bind filename %s\n", cliaddr.sun_path);
while ((size = read(cfd, buf, sizeof(buf))) > 0) {
for (i = 0; i < size; i++)
buf[i] = toupper(buf[i]);
write(cfd, buf, size);
}
close(cfd);
}
close(lfd);
return 0;
}client
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <sys/un.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include "wrap.h"
#define SERV_ADDR "serv.socket"
#define CLIE_ADDR "clie.socket"
int main(void) {
int cfd, len;
struct sockaddr_un servaddr, cliaddr;
char buf[4096];
cfd = Socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
bzero(&cliaddr, sizeof(cliaddr));
cliaddr.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(cliaddr.sun_path,CLIE_ADDR);
len = offsetof(struct sockaddr_un, sun_path) + strlen(cliaddr.sun_path); /* 计算客户端地址结构有效长度 */
unlink(CLIE_ADDR);
Bind(cfd, (struct sockaddr *)&cliaddr, len); /* 客户端也需要bind, 不能依赖自动绑定*/
bzero(&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr)); /* 构造server 地址 */
servaddr.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
strcpy(servaddr.sun_path, SERV_ADDR);
len = offsetof(struct sockaddr_un, sun_path) + strlen(servaddr.sun_path); /* 计算服务器端地址结构有效长度 */
Connect(cfd, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, len);
while (fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin) != NULL) {
write(cfd, buf, strlen(buf));
len = read(cfd, buf, sizeof(buf));
write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, len);
}
close(cfd);
return 0;
}